December 18th is declared as the International Migrants Day every year since 2000 by the United Nations General Assembly. The International Migrants Day has been recognised as a day to reflect on the role of migrants in our societies, their positive contributions and the challenges they face in achieving their full potential and capabilities.
This day is also a reminder that human rights are not ‘earned’ by virtue of being a hero or a victim, but are an entitlement for everyone, regardless of origin, age, gender and status. Migration is a dynamic phenomenon, constantly requiring policy interventions in order to maximize its potential benefits and minimize related costs in the context of socio-economy of the migrants' place of origin and destination.
Be it for work, to join family, to study, to upgrade quality of living or to escape conflicts or in response to the adverse effects of climate change or natural disasters, or other environmental factors, humanity has been constantly on the move. Today, more people than ever are migrants.
According to the World Migration Report 2022, globally, as of 2019, the number of international migrants was estimated to be almost 281 million (which is 3.6 per cent of total population), 128 million more than what was in 1990. Out of this, 169 million were migrant workers, up from 164 million in 2017. Nearly, 20 per cent of the migrants originate from South Asia, including India, which accounts for the largest number of migrants living abroad (18 million).
The Covid-19 pandemic restricted the movement as well as migration both globally and locally. In the aftermath of the Covid-19, the international migration has started once again across the globe.
The Migration in India Report 2020-21 of the National Statistical Office (NSO) suggests that in the aftermath of Covid-19, in India, the migration rate was 28.9 percent for in-migrants. According to Government of India (GoI) estimates, India being a country of more than 135 crore, 39 crore are migrants. The estimate is based on the survey of members of the households at Place of Enumerations (PoE) on in-migrants whose PoE is different from their last UPR (Usual Place of Residence).
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) data on migration also reported that out of total migrants, the share of international migrants would be less than one percent (0.75 percent, as unit level data) whose last UPR was another country at current PoE and estimated to be 2.9 million approximately, which means nearly 3 million persons in India are international in-migrants during 2020-21.
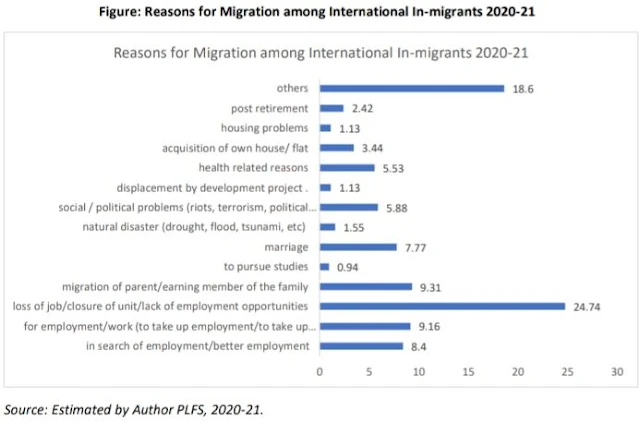
The estimates also suggest that out of total international migrants, nearly a quarter of them (24.7 percent) have left their UPR (which was in a country other than India) due to job loss/ lack of employment opportunity in another country in which they were residing prior coming to India.
This day is also a reminder that human rights are not ‘earned’ by virtue of being a hero or a victim, but are an entitlement for everyone, regardless of origin, age, gender and status. Migration is a dynamic phenomenon, constantly requiring policy interventions in order to maximize its potential benefits and minimize related costs in the context of socio-economy of the migrants' place of origin and destination.
Be it for work, to join family, to study, to upgrade quality of living or to escape conflicts or in response to the adverse effects of climate change or natural disasters, or other environmental factors, humanity has been constantly on the move. Today, more people than ever are migrants.
According to the World Migration Report 2022, globally, as of 2019, the number of international migrants was estimated to be almost 281 million (which is 3.6 per cent of total population), 128 million more than what was in 1990. Out of this, 169 million were migrant workers, up from 164 million in 2017. Nearly, 20 per cent of the migrants originate from South Asia, including India, which accounts for the largest number of migrants living abroad (18 million).
The Covid-19 pandemic restricted the movement as well as migration both globally and locally. In the aftermath of the Covid-19, the international migration has started once again across the globe.
The Migration in India Report 2020-21 of the National Statistical Office (NSO) suggests that in the aftermath of Covid-19, in India, the migration rate was 28.9 percent for in-migrants. According to Government of India (GoI) estimates, India being a country of more than 135 crore, 39 crore are migrants. The estimate is based on the survey of members of the households at Place of Enumerations (PoE) on in-migrants whose PoE is different from their last UPR (Usual Place of Residence).
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) data on migration also reported that out of total migrants, the share of international migrants would be less than one percent (0.75 percent, as unit level data) whose last UPR was another country at current PoE and estimated to be 2.9 million approximately, which means nearly 3 million persons in India are international in-migrants during 2020-21.
The estimates also suggest that out of total international migrants, nearly a quarter of them (24.7 percent) have left their UPR (which was in a country other than India) due to job loss/ lack of employment opportunity in another country in which they were residing prior coming to India.
This seems to be a major cause of concern for the country, as it would adversely impact on the remittances from other countries. As per the World Bank’s Migration and Development Brief, India was a recipient for remittance to the tune of $89 billion in 2021, and remained the top recipient among the low- and middle-income countries category. The amount of remittance has been on rapid rise since 2005.
However, more recently, around 18 percent migrated to India from another country in order to search an employment/ better employment/ or to work in India, which means they consider India a better place to get a work opportunity as per their aspirations. Another important reason for migration among the international migrants was migration of parents/ earning members of the family.
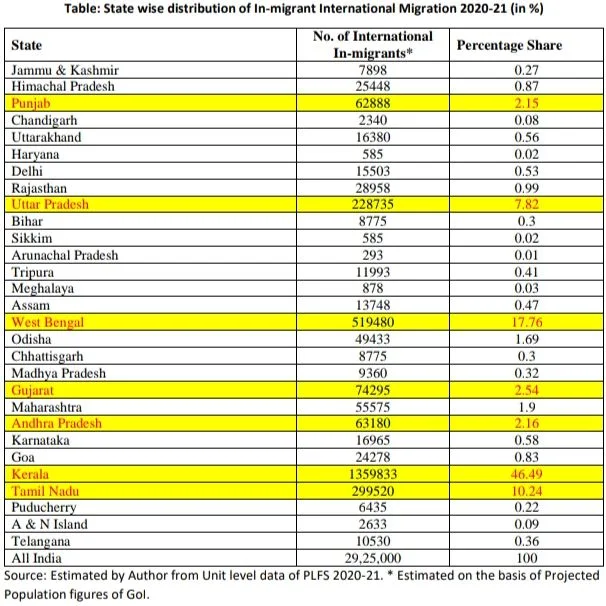
Further, the State-wise distribution of such international in-migrants depicts that Kerala has been the State of highest number of international in migrants with a share of 46.5 percent followed by West Bengal (17.8 percent), Tamil Nadu (10.2 percent), Uttar Pradesh (7.8 percent) and Gujarat (2.5 percent).
---
*Respectively: assistant director and deputy director, National Institute of Labour Economics Research & Development (NILERD), under NITI Aayog, Government of India. Views are personal
Further, the State-wise distribution of such international in-migrants depicts that Kerala has been the State of highest number of international in migrants with a share of 46.5 percent followed by West Bengal (17.8 percent), Tamil Nadu (10.2 percent), Uttar Pradesh (7.8 percent) and Gujarat (2.5 percent).
---
*Respectively: assistant director and deputy director, National Institute of Labour Economics Research & Development (NILERD), under NITI Aayog, Government of India. Views are personal



Comments